Retail Inventory Tracker 2025 – Free Retail Inventory Management Template
I am glad to present a simple and effective way to manage orders and inventory for your retail business. If you are getting started with a retail business where you plan to buy products from your suppliers and then sell them to customers with a margin, then you would need a tool to track your business in an effective way.
This Excel template is designed for Microsoft Excel, but if you are looking for a Google Sheet template, please visit Retail Inventory Tracker in Google Sheets.
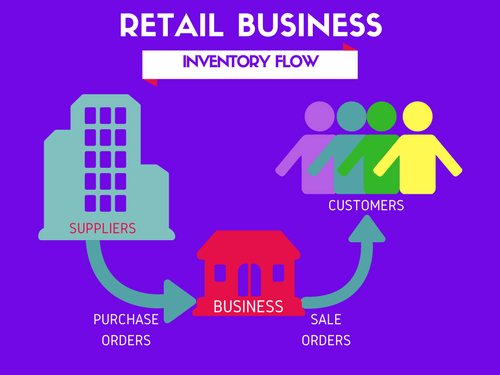
Why do we need an Inventory and Sales Management tool?
I am sure you will agree that you need to know the following information in order to manage your business better.

- How many items you currently have in inventory of each product so that you can take orders from your customers accordingly? If you cannot fulfill orders from your customers on time, you will be losing credibility as a business.
- Which products are low in inventory (compared to a Re-order point)? This helps in deciding when and what to buy in purchase orders to your suppliers.
- Which products are selling well and which products are not? This will help you decide to buy profitable products and not buy those that are not.
- What is the profit/loss you make from your business? This is obvious. If you are not turning in profit, you need to improve the business strategy.
- Who are the best customers and best suppliers? Building great relationships with the suppliers who bring in most revenue will be helpful. Providing special service to your best customers will likely result in more sales in future.
In order to get to this information easily and quickly, we need some kind of software. There are several sophisticated and expensive cloud based software available to manage inventory and sales for retail businesses.
For small and medium size businesses, especially when we are starting up, it is important that any software we choose is easy to use, customize and not expensive. This is why I am excited to present a free Excel template as a solution.
This template is a follow up to the most popular template on indzara.com – Inventory & Sales Manager. This new template provides several improved features but I have decided to keep the older template online as well. For example, this new template has automatic price population on order line items which the old one doesn’t. There are some users who do not want to auto-populate the prices as they want flexibility to change prices for different customers. For those, the old template would be useful. Hence, it would be better to have both templates available to our users.
Features of Retail Inventory Tracker Excel Template

Order Management
- 3 types of orders (Sale, Purchase, Adjust)
- Handles product returns
- Auto-Populate product prices in orders
Inventory Management
- Calculates current inventory of each product
- Set re-order points and know what to order
Finance
- Handles tax
- Handles product level and order level discounts
- Calculates Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) and Profit
Data Management
- Easily access Product, Partner (Customer and Supplier) and Order Lists
- Maintain history of Product price data
Reporting
- 6 page interactive report of business metrics
- 12 month trends of key metrics
- Identify best products and partners
- Calculates Inventory value
Video Demo
How to Use Retail Inventory Tracker
Before we get started, I highly recommend reading these articles if you are new to Excel templates or Excel Tables.
- Important tips about using Excel Templates from indzara.com
- Do not edit calculated cells (ones with formulas).
- Input data is always visible and can be edited easily.
- Backup by saving copies of this file regularly.
- Introduction to Excel Tables (How to use Excel tables to enter data)
To make it easy for you to identify which fields are input fields, calculated and custom fields, I have followed the following color scheme in column headings (or labels).
- Color Legend for this template
- Columns with Purple colored labels – Input cells for user to enter pre-defined information.
- Columns with Green colored labels – Calculated cells. Should not be edited.
- Columns with Blue colored labels – Custom Input cells for user to store any information needed.
Overview of steps
- Initial Setup
- Enter Business Information in Settings sheet
- Enter Product Categories in Settings sheet
- Enter list of Products in Products sheet
- Enter current Prices of products in Prices sheet
- Enter list of customers and suppliers in Partners sheet
- Creating Orders
- Enter list of Orders in Order Headers sheet.
- Enter each order’s details (line items) in Order Details sheet.
- Viewing business report
- View summary of business performance in Report sheet
Detailed Step by Step instructions (with screenshots)
Initial Setup
These Initial Setup steps are to be done first as a one-time activity.
Step 1: Enter Business Information
In Settings sheet, Enter your business information such as address, email and phone number.

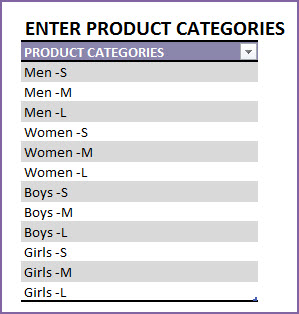
Step 2: Enter Product Categories
If you are selling several products in your business, it is recommended that you categorize your products. This helps a lot in managing them and understanding their sales performance.
Step 3: Enter Products
It’s time to enter our products. In the Products sheet, let’s enter each of our products in a separate row.
Please start entering from row 4
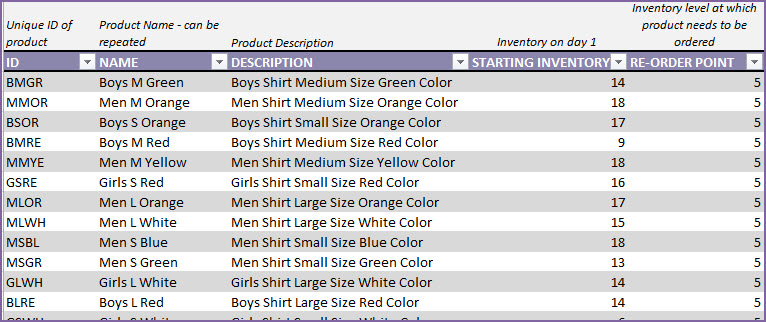
Let’s see each of the fields in the Products table.
- ID: Unique identification of product. This has to be unique. Please do not repeat the same ID or leave the field blank.
- NAME: Name of the product
- DESCRIPTION: Description of the product, as needed in our business.
- STARTING INVENTORY: This is the quantity of the product we have when we begin using the template. This is entered only once and does not have to be updated daily.
- RE-ORDER POINT: The quantity of product at which you would like to replenish by ordering.
There are a few more columns of product information we can input.
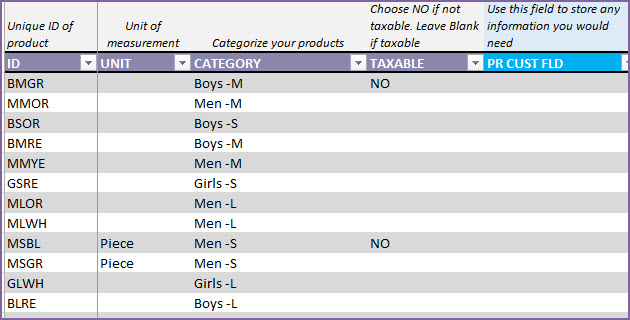
- UNIT: This is how we measure this specific product.
- CATEGORY: Product category to which this product belongs.
- TAXABLE: In our business, if we have products that are not taxable, we can enter NO. If tax is applicable, just leave it blank. By default, tax will be applicable.
- PR CUST FIELD: This field is provided as a placeholder for you to enter any information you need at Product level. You can rename the field and use it as needed.
The other columns in this sheet are all calculated columns. We will discuss more about this later in this article.
The columns that have Green colored labels are all calculated columns. Please do not edit the formulas in them.
Step 4: Enter Product Prices
In Prices sheet, we will be entering Purchase and Sales prices. This information will be used to auto-populate prices in our orders. This will save a lot of time in data entry of orders.
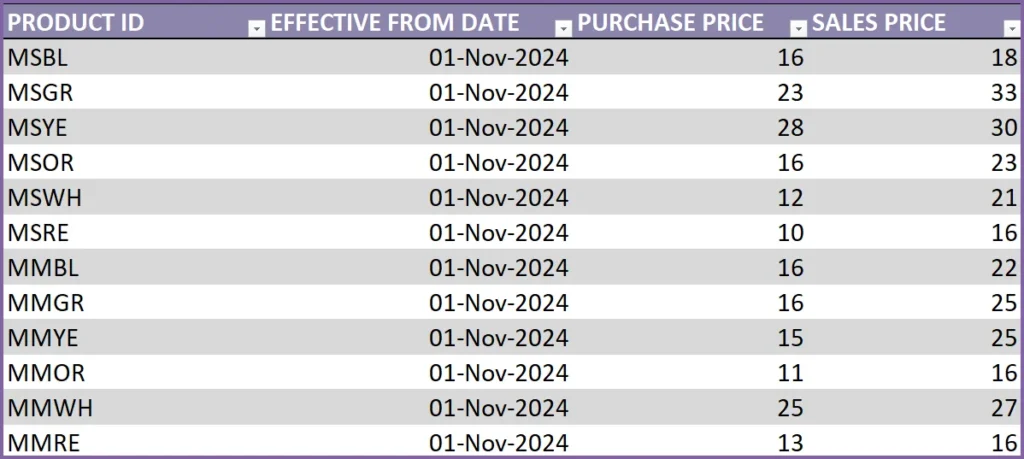
Purchase Price is the price we pay our suppliers to purchase products. Sales Price is the price we sell the products to our customers at.
To begin with, let’s assume we start using this template from Nov 1, 2024 to enter orders.
We enter each product in this Prices table and enter Nov 1, 2024 as the Effective Date. The Purchase and Sales prices we enter will be the prices effective as of Nov 1, 2024.
What if price changes?
The template is designed to accommodate price changes for products. You may have an increase in prices of certain products over time. Not a problem.
If price changed for a product from Jan 1, 2024, we will just add a new row, enter the Product ID, Effective date (as 01-Jan-2024) and the new Purchase and Sales prices. Please note that we have to add new rows whenever prices change, and not to replace the older data.
We have to enter both purchase and sales price in each row, even if only one of them changes.
Step 5: Enter list of Partners
In the Partners sheet, we store the list of our partners. Partners include Suppliers and Customers.
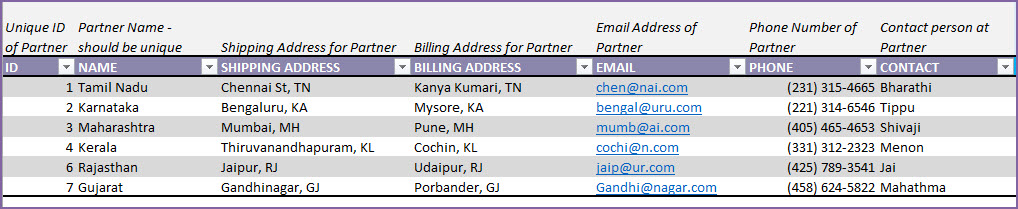
If a partner is both a customer and a supplier (it is possible in some scenarios), enter the partner only once.
- Partner ID and Partner Names should be unique.
- Enter Shipping and Billing address, E-mail address and Phone number.
- Enter the primary person of contact for each company in the CONTACT field.
This sheet now serves as a nice organized set of data about your partners.
We have completed the initial set up now. It’s time to enter our first order.
Creating Orders
Before we enter our order, let’s learn about the types of orders. You can create 3 types of orders in this template.
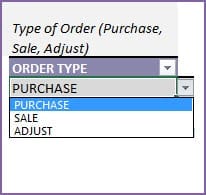
- PURCHASE: When we purchase products from our suppliers, we enter a PURCHASE order. This order will add the purchased items to inventory on the Expected Date.
- SALE: When we sell products to our customers, we enter a SALE order. This order will subtract sold items from the inventory on the Expected date.
- ADJUST: We can create an ADJUST order and enter negative quantity values to reduce inventory or positive values to increase inventory as needed. This can be used to adjust our inventory numbers to ensure that the numbers match the inventory on hand. For example, we may lose products due to damage or expiry or other reasons. We would want to adjust our inventory accordingly and that’s where we can use ADJUST order type.
Creating a Purchase Order
Orders are entered in this template in 2 stages – 1) Order Header and 2) Order Details. Let’s use an example. The products here are shirts for boys and girls. They are available in different colors.
In the Order Headers sheet, we enter the following information.
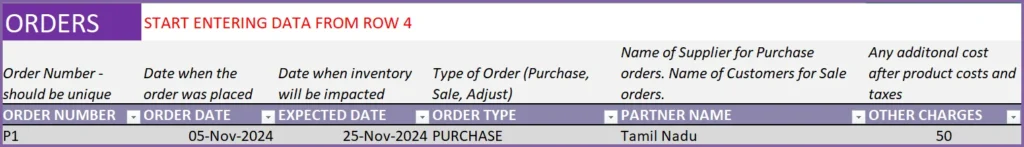
The Order Number should be unique. In other words, each order should be entered in one and only one row. The field should not be blank.
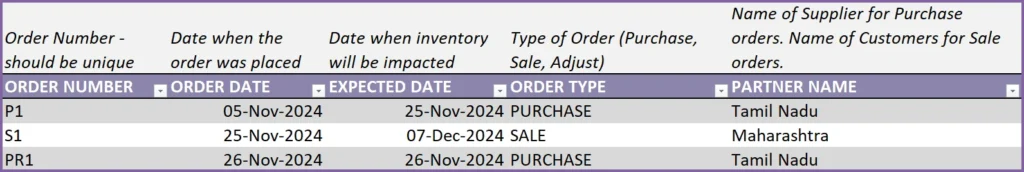
We can enter any method of numbering orders. The template does not limit that and does not create any pre-defined order numbers. Here, we have entered ‘P1’ as order number, to reflect that it is the first purchase order we are entering.
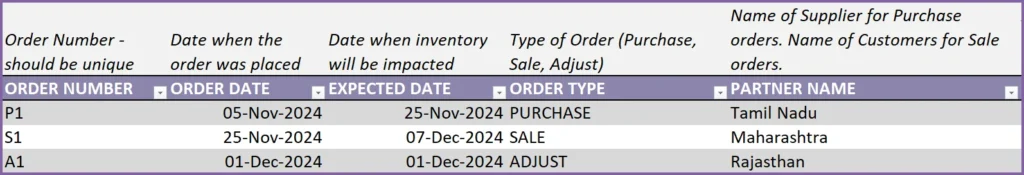
Order Date and Expected Date
Each order will have 2 dates. Order Date and Expected Date. Order Date is the date when the order is placed. Expected Date is the date when the inventory is impacted.
For example, if you place a purchase order on Nov 5th. The supplier says the products will reach your inventory on Nov 25th. Here, Nov 5th is Order Date and Expected Date is Nov 25th. If there is a delay later and the supplier says it will only reach on Nov 27th, then we have to update the Expected Date of our order to Nov 27th.
Order Type is ‘Purchase’ and we have chosen our supplier in the Partner Name field.
There are additional information we can enter in the Order Header.
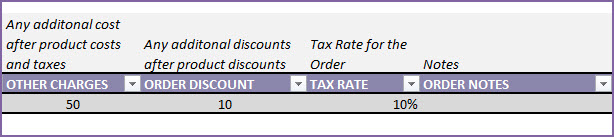
- OTHER CHARGES: Any additional cost on the order. For example, shipping charges.
- ORDER DISCOUNT: Any additional order level discount amount (not %). We will be entering product level discounts later.
- TAX RATE: Tax Rate % applicable for this order. We can have different tax rates for different orders.
- ORDER NOTES: Enter any notes for your reference to this specific order.
Now, we enter the items on the order in the Order Details sheet.
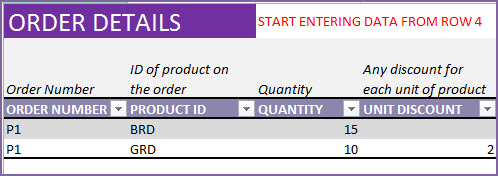
It is very simple. Enter Order Number, Product ID, Quantity and any Unit Discount.
Here, we have entered a purchase order to purchase 15 units of Boys Shirt in Red color and 10 units of Girls Shirt in Red color. There is a discount of $2 (any currency you use) for each of the 10 Girls shirts and no discounts for the Boys shirts.
The template will calculate amounts for each line item. Let’s understand how the calculations work.
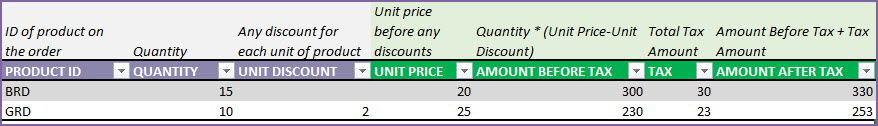
Unit Price is automatically pulled over from the Prices sheet. Price chosen will be the one that was effective as of the Order Date of the order.
BRD (Boys Shirt – Red color)
- Amount Before Tax = Quantity * (Unit Price – Unit Discount) = 15*(20-0) = 300.
- Tax = 10% of 300 = 30
- Amount After Tax = 300 + 30 = 330
GRD (Girls Shirt – Red color)
- Amount Before Tax = Quantity * (Unit Price – Unit Discount) = 10*(25-2) = 230.
- Tax = 10% of 230 = 23
- Amount After Tax = 230 + 23 = 253
This purchase order will automatically update the inventory by adding 15 units to BRD and 10 units to GRD. We can view the inventory levels in two places in this template. One is the Report sheet. Another is the Products table. We will cover these later in the Reporting section below.
Creating a Sales Order
Entering a sales order is very similar to the purchase order, except that our Order Type is ‘Sale’ now.
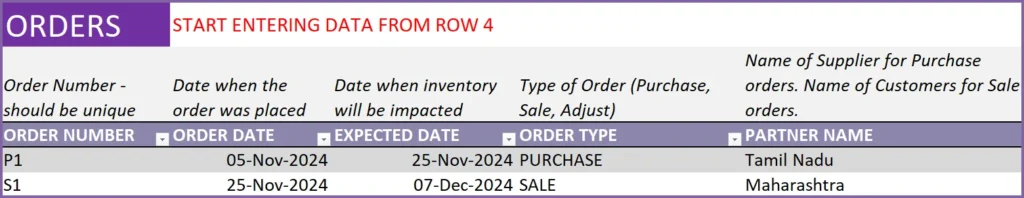
As shown in the image above, to add an order, we just add our entry in a new row in Order Headers sheet.
We enter S1 as Order Number. This sale order was placed on Nov 26th and products were given to customer on the same day (Nov 26th).
In the Order Details sheet, we add 2 rows as we are selling two products (BRD and GRD). 10 units of BRD and 5 units of GRD.
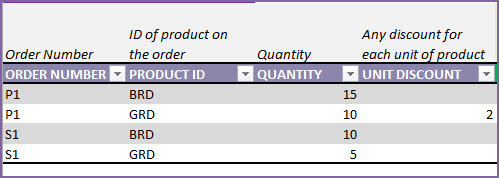
This order will now automatically reduce inventory for each of the products, effective as of Nov 26th (Expected date).
Handling Supplier Return
If we have a situation where we want to return products back to our supplier due to some reason (example: defective products), we can do so easily.
We will enter a new Purchase order.
Tip: For easier identification of return orders, you can enter order number differently. For example, use a prefix of PR for purchase return orders.
In our example, after receiving the products on Nov 25th, we notice that there are 5 defective BRD units. We want to return them.
So, on the next day (Nov 26th), we send the products back to the supplier.
In the Order Details sheet, we will enter the information on returning product and quantity.
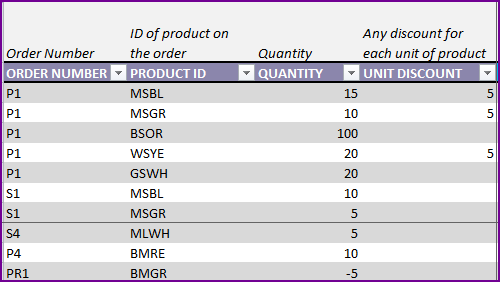
Since we are returning 5 units of BRD, I have entered -5 as Quantity. Entering a negative value is important. That ensures that our inventory is reduced by 5 units for this product.
Handling Customer Return
Similar to the Supplier Return, we can also handle customer returns. If customer decided to return products to us, we can enter that information in the template. We use a Sale order for that purpose.
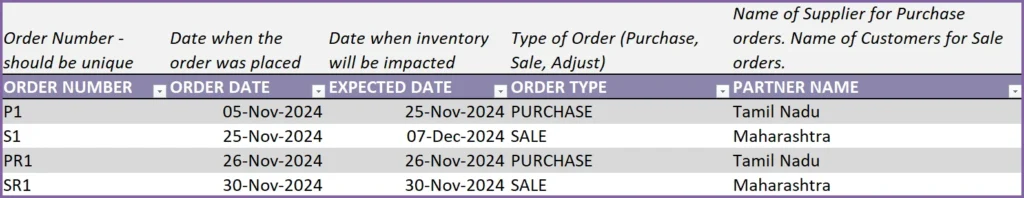
In this example, SR1 is the sale return order that is placed on Nov 30th.
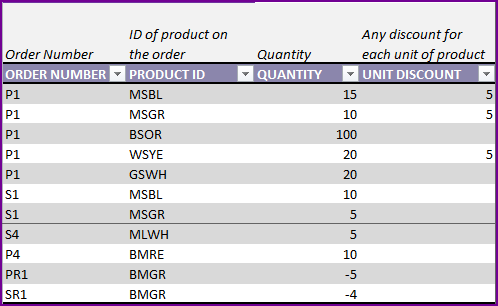
4 units of GRD are returned by the customer. We enter -4 as Quantity. This will be used by the template to add 4 units to GRD inventory, effective as of Nov 30th.
Creating an ADJUST order
On some occasions, we may find that a product is either expired or damaged locally at the warehouse. We cannot return it to the supplier, and we cannot sell that to customer too. We need to make sure that our current inventory calculations reflect the true available inventory to sell. This is where we can use the order type ‘Adjust’.
In the Order Headers sheet, we first create a new Adjust order.
For example, one GRD shirt was damaged in the warehouse and we notice it on Dec 1st. So, we enter it as shown below.
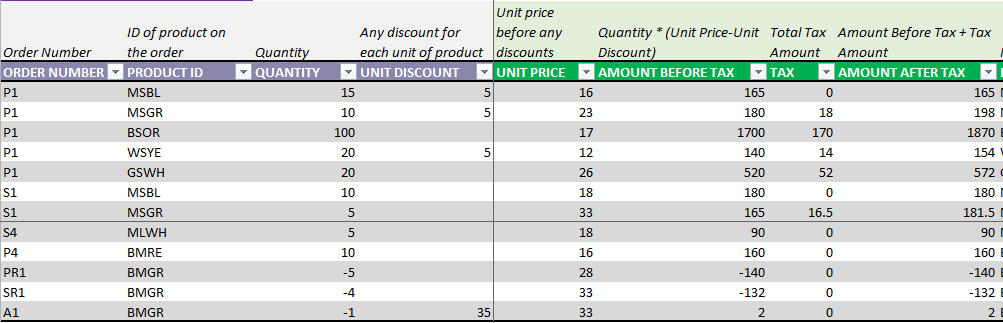
We enter -1 as Quantity. This will reduce the inventory by 1.
If we want to increase inventory levels without entering a purchase order, we can use an ADJUST order where we enter positive values as Quantity.
We enter 35 as Unit Discount (as that is the sales price of the product). This is to zero out the impact on cost. If we are not incurring any additional cost by disposing the shirt, then this method is recommended.
If we incur any additional cost, then we enter the appropriate Unit Discount so that the total Amount after Tax reflects the disposal cost.
Business Performance Reporting
The template has extensive automated and interactive reporting in the Report sheet.
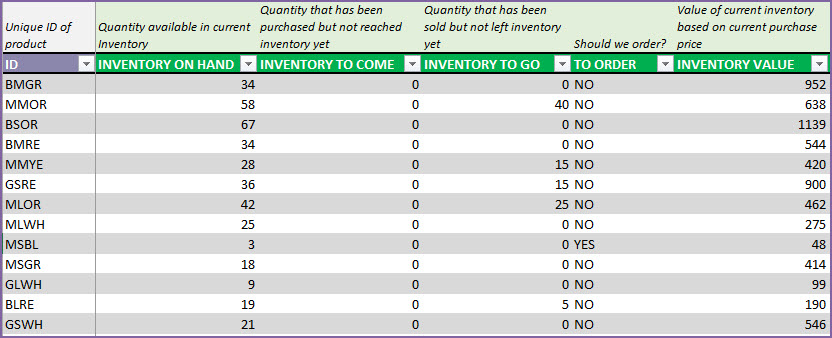
Current Status (Inventory level and Inventory value)
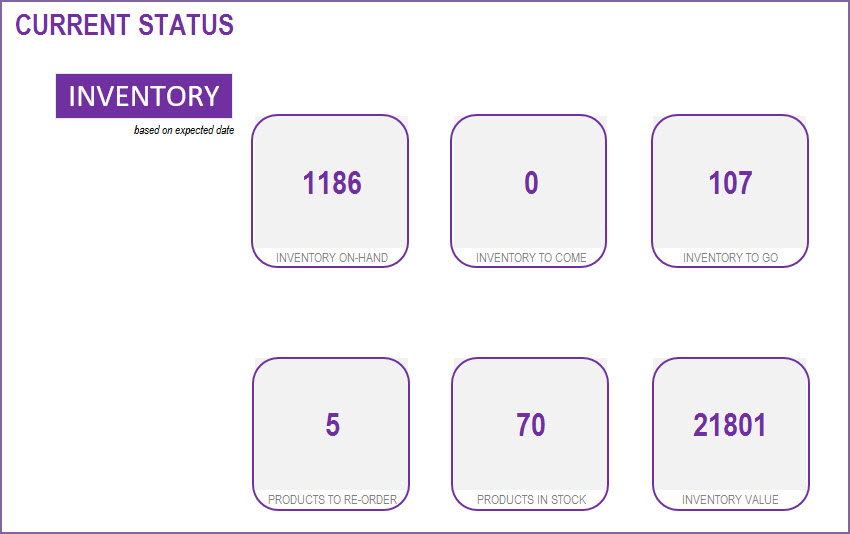
The following metrics are displayed to reflect the status as of today.
- Total inventory (quantity) on hand
- Total inventory to Come (ordered from suppliers already and will reach our inventory in future)
- Total inventory to Go (ordered by customers already and will leave our inventory in future)
- Number of Products to re-order (products whose current inventory is at or below its Re-Order Point)
- Inventory Value (calculated based on current purchase price of the products on hand)
The above presents the overall summary of all products together. We would also want to see this information individually for each product. To do that, we go to the Products sheet.
Now, the rest of the Report sheet presents an interactive way of accessing business performance metrics.
We can customize the date range for the report by choosing any start and end dates.

We leave the Refresh as ON. If you enter a lot of order data over time and if you notice the file is getting slower, you can turn this OFF. It will stop the report from refreshing constantly and that will improve performance.
For the date range we entered, we can see the summary metrics.
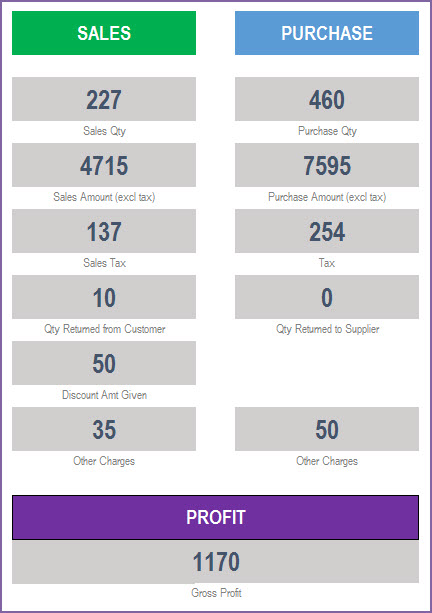
- SALES
- Sales Qty: Total of quantity on Sale orders. Considers returns as well.
- Sales Amount: Total Order amount on the Sale orders. Includes product level discounts. Does not include tax, order level charges and order level discounts.
- Sales Tax: Total tax amounts on Sale Orders
- Qty Returned from Customer: Quantity returned by customers
- Discount Amt Given: Total amount of discount given to customers
- Other Charges: Total of other charges on all Sale orders
- PURCHASE
- Purchase Qty: Total of quantity on Purchase Orders. Considers returns as well.
- Purchase Amount: Total Order amount on the purchase orders. Includes product level discounts. Does not include tax, order level charges and order level discounts.
- Tax: Total tax amounts on Purchase Orders
- Qty Returned to Supplier: Quantity returned to suppliers
- Other Charges: Total of other charges on all Purchase orders
- PROFIT
- Gross Profit: Sales Amount – Cost of Goods Sold
- Cost of Goods Sold is the sum of purchase price of products sold. Purchase price is the price of product as of Sale order date.
- Gross Profit: Sales Amount – Cost of Goods Sold
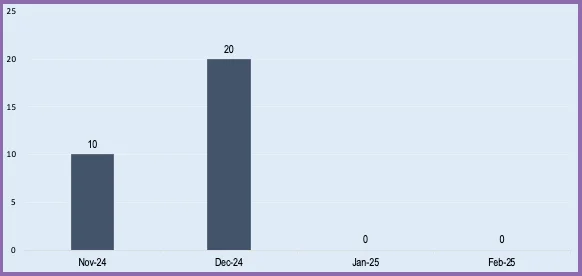
We can view these metrics by month, for 12 months at a time.
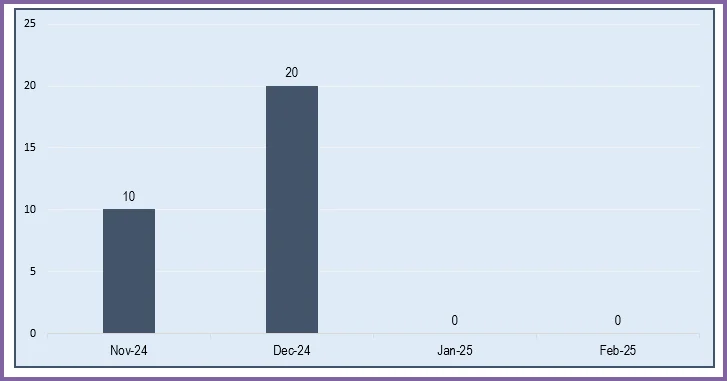
We can choose one of the metrics to display data on a chart showing trends over 12 months.
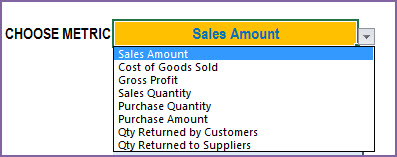
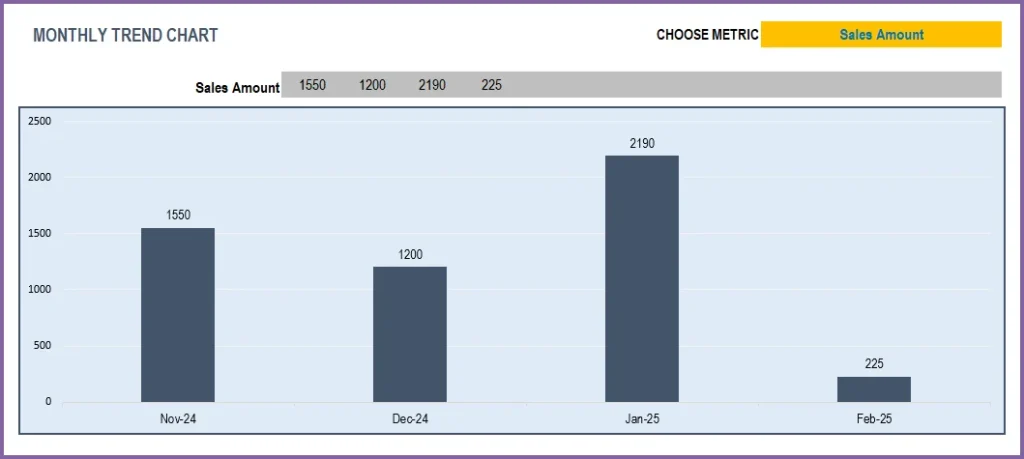
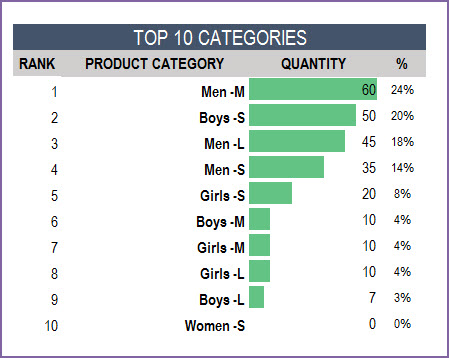
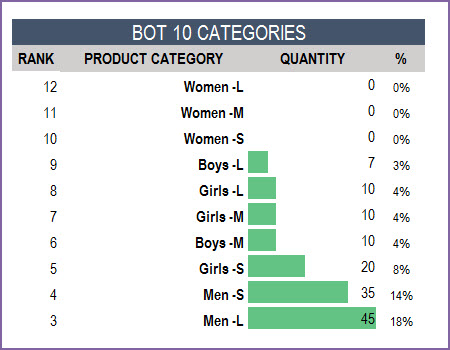
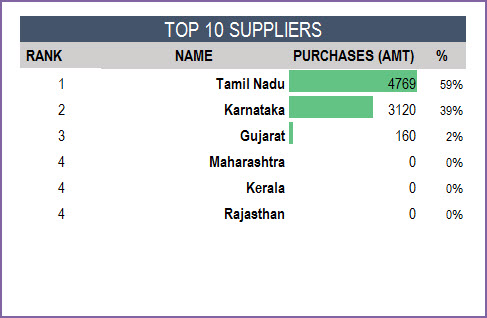
Top 10 and Bottom 10 Products
One of the important pieces of understanding business performance is knowing which products are selling the most and which ones are not. We have 3 ways of measuring sales – Quantity, Amount and Margin. This allows us to understand the true impact of the products to the business.

We will see top 10 and bottom 10 Product Categories by the selected Sales metric.
Similarly, the top 10 and bottom 10 Products by sales metric.
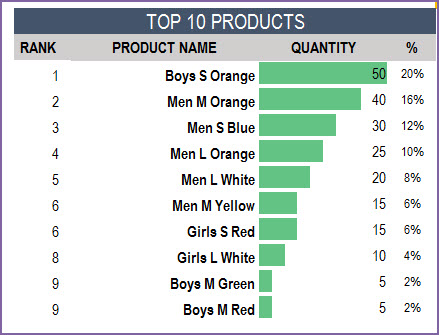
If we want to look for details of a specific product, we can choose the product ID from the drop down.


Partner Performance
Another important aspect is to understand best partners (customers and suppliers).
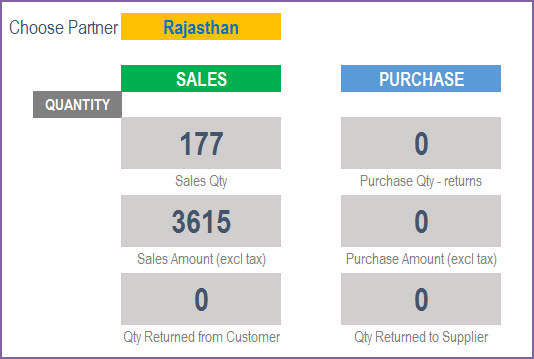
We can then see the details of one specific partner at a time.
Use this retail inventory template to handle all your inventory management requirements. If more details are required please visit customer support for this retail inventory management excel template.
Recommended Templates
For more features like
- Invoice Generation (Customizable design)
- Checks inventory availability in invoice
- Purchase Order Generation
- Accounting – Track payments made and payments due
-
 Retail Business Manager – Excel TemplateOriginal price was: $50.$40Current price is: $40.
Retail Business Manager – Excel TemplateOriginal price was: $50.$40Current price is: $40. -
 Retail Business Manager (Pro) – Excel Template (Multiple Locations)$50
Retail Business Manager (Pro) – Excel Template (Multiple Locations)$50 -
 Retail Business Manager – Google Sheet TemplateOriginal price was: $50.$40Current price is: $40.
Retail Business Manager – Google Sheet TemplateOriginal price was: $50.$40Current price is: $40.

210 Comments
Hello
Send Me Files through n2bra@yahoo.com
Hello
We have shared the file. Meanwhile, please let us know what issues you faced while downloading the template from the webpage.
Best wishes
i am using your templates it is very usefull for us i am using retail inventory tracker but i am having problem in price collum our price are changed client to client not date to date how could i adjust it in sale price because when i set the sale price twice on same date last price are subject to change on all same date customers but my customers sale price are different
Thanks for using our template.
Please ensure that none of the formulas of links are broken. You may download the template again. In case the issue persists. Please email your template with the list of issues to contact@indzara.com
Best wishes
Hello Dear
Send Me Files through JavedIbrahimi24@gmail.com
Hello
We have shared the template through email.
Best wishes
Hi Dear
How can I take the template copy and save it in my Pc
Hello
You may prepare copies of the template.
Best wishes
Hi there, i am having issues with the report section of my excel sheet. I wish I can screen-grab it to explain better. I have imputed all the fields correctly. But the Report section is not updating. It still has same information as at when I downloaded it.
Thanks for using our template.
Please send your file along with the list of issues to contact@indzara.com
Best wishes
Hello,
Great template, I’ve been using it for a while now but column headings no longer stay on top of the page when I scroll down.
Also, I am using two copies of this workbook to track two separate warehouses that stock the same inventory. If I upgrade to your paid version that allows multiple warehouses, will I be able to transfer over my data easily?
Thanks
Thanks for using our template.
You may freeze the top rows to keep the column heading visible.
You have to enter the data manually to the new file.
Best wishes
Send file to this Email: marakthorng123@gmail.com
Hello, thank you for this template. I just downloaded it and the formulas in the Inventory to come and the Inventory to go do seem to be working. I have completed the spreadsheet as instructed and refreshed, but they are still at a 0.
Thx,
Melissa
Thanks for using our template.
Please share your file along with the list of issues to contact@indzara.com
Best wishes
file are not downloading. please send me on zafarasim9315@gmail.com
Thanks
Hello
We have sent the file through email.
Thanks
Hi Indzara,
First of all, thank you for sharing this great template.
I’m using your free retail inventory management template and it was running fine for almost 2 months.
But suddenly, this morning I found out from the report page that some of the data value was not populating the correct sales prices which suppose remains used the ‘effective from date’ in the Prices sheet.
How could I fix it in the Order Headers & Order Details to pick up the correct prices again?
I’m sorry, it was my bad. i found my mistakes, please disregard my message.
Thank you for the file!!